What is Vaginal Tightening?
Vaginal tightening refers to any method used to tighten the vagina, which can lose muscle tone and become lax after childbirth or menopause or due to age.
Most women have no issues with the size, lubrication, or elasticity of their vagina post-childbirth or as they age. But for others, problems such as sexual dysfunction, vaginal atrophy, vaginal laxity, painful intercourse, and stress incontinence can hurt their quality of life.
Benefits of Vaginal Tightening
- It improves the symptoms of vaginal atrophy, where the vaginal walls become thinner, drier, and inflamed.
- Reduces feminine dryness.
- Treats stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
- Improves lubrication
- Reduces the number of recurrent infections such as Bacterial Vaginosis (BV).
- Improves vaginal laxity.
- Increases sexual pleasure for both partners.
Methods of Vaginal Tightening
Treatment options include the following:
- Invasive Vaginal Surgery and Laser
- Yoga and Exercise
- Non-invasive topical products: using astringent ingredients.
Invasive Vaginal Surgery and Laser
Several types of tightening surgeries are available, each addressing different aspects of vaginal laxity. Traditional vaginoplasty is the most common form, which involves making an incision in the perineum, tightening the muscles and tissues, removing excess tissue, and closing the incision with sutures. Laser vaginal rejuvenation uses lasers to make incisions and tighten muscles and tissues, offering greater precision, reduced scarring, and faster recovery than traditional vaginoplasty. On the other hand, perineoplasty focuses on the perineum area, tightening muscles and tissues, and can be combined with vaginoplasty.
Vaginal Surgery and Laser can take up to six weeks to recover from and have associated risks such as scarring, loss of sensation, bleeding, infection, or skin necrosis (skin death).
Non-Invasive Topical Products
LibiTight Femme Gel (Libi -Tight Femme Gel 30g) contains several ingredients that help with vaginal tightening:
- Hyaluronic Acid: Helps restore tissue elasticity and facilitates tissue regeneration, providing a firming and tightening effect.
- Arginine: An antioxidant that supports anti-aging and collagen production, which can improve the structure and tightness of vaginal tissues.
- Allantoin: Acts as an astringent ingredient, helping to strengthen and tighten vaginal tissues.
- Potassium Alum (1.5%): A natural astringent that assists in tightening the vaginal walls, providing a firmer feel.

Yoga and Exercise for Vaginal Tightening
Specific exercises and yoga poses can specifically target the pelvic floor muscles, which support the vagina and contribute to its tightness. These exercises and poses can help improve vaginal tightness and overall vaginal health. Here are some exercises and yoga poses and their benefits:
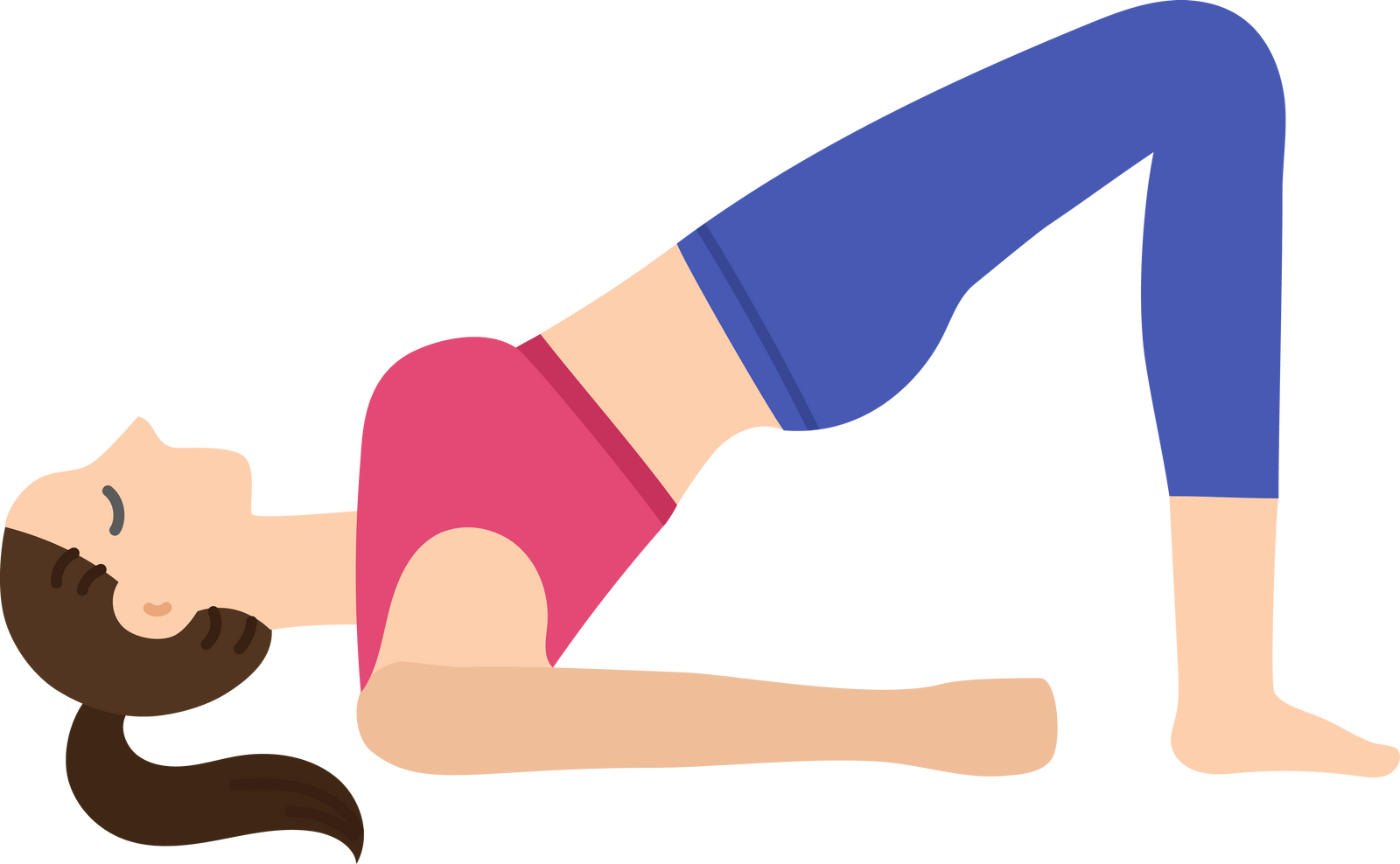
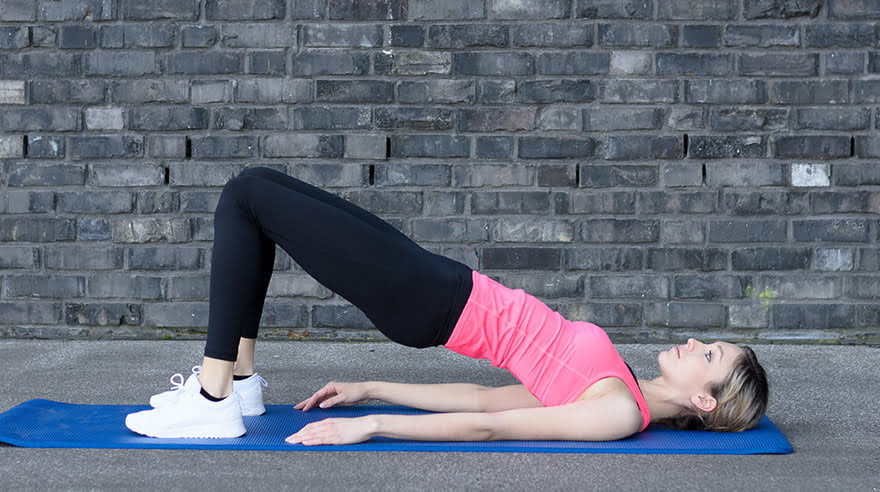
Bridge Pose: This posture fortifies the pelvic floor muscles, glutes, and hamstrings while offering a mild stretch for the hip flexors.

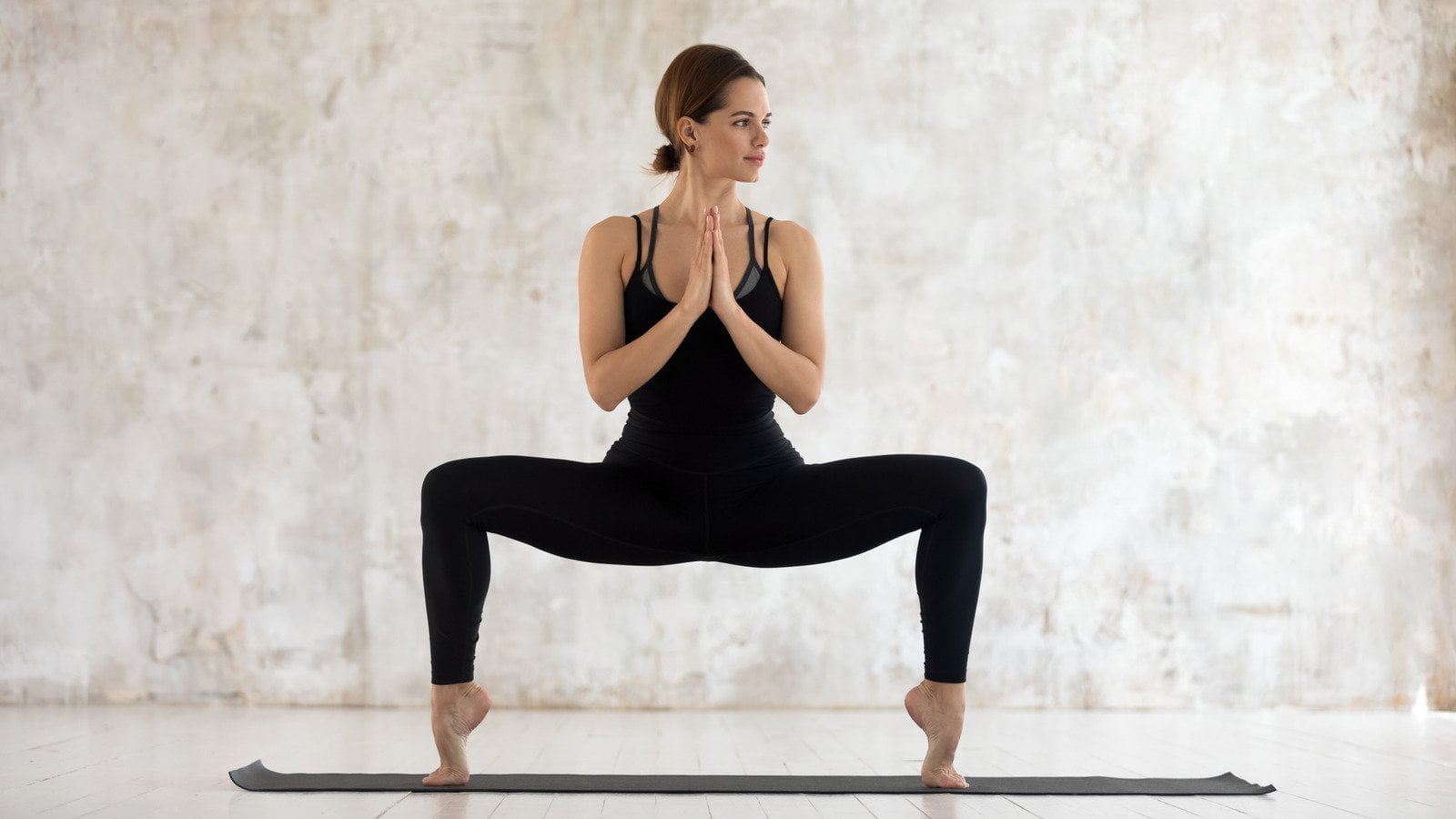
Goddess Pose: Targets the pelvic floor, inner thighs, and glutes, helping to strengthen and tone these muscles.

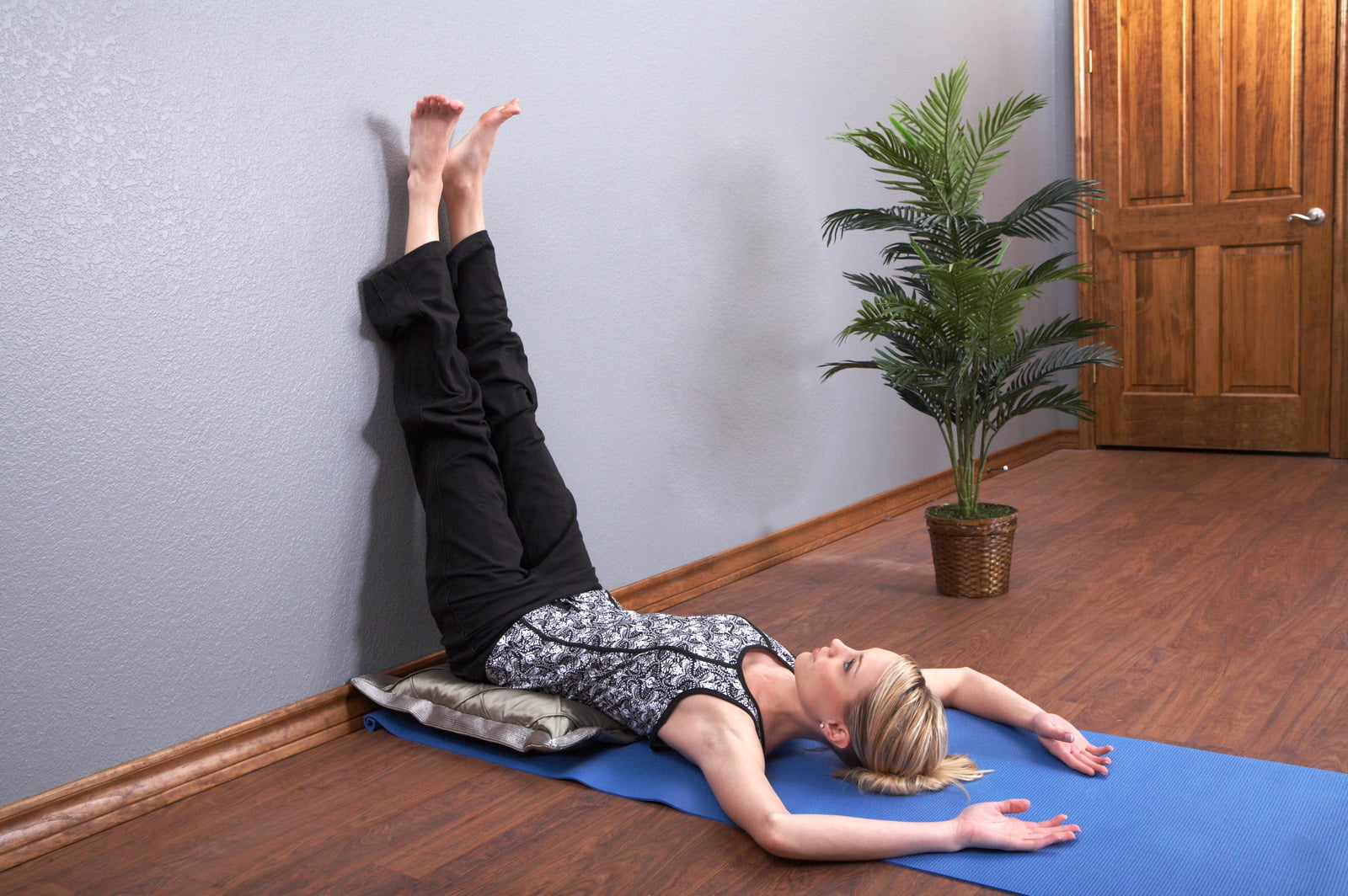
Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose: Helps improve circulation in the pelvic region and promotes relaxation, which is beneficial for overall vaginal health.

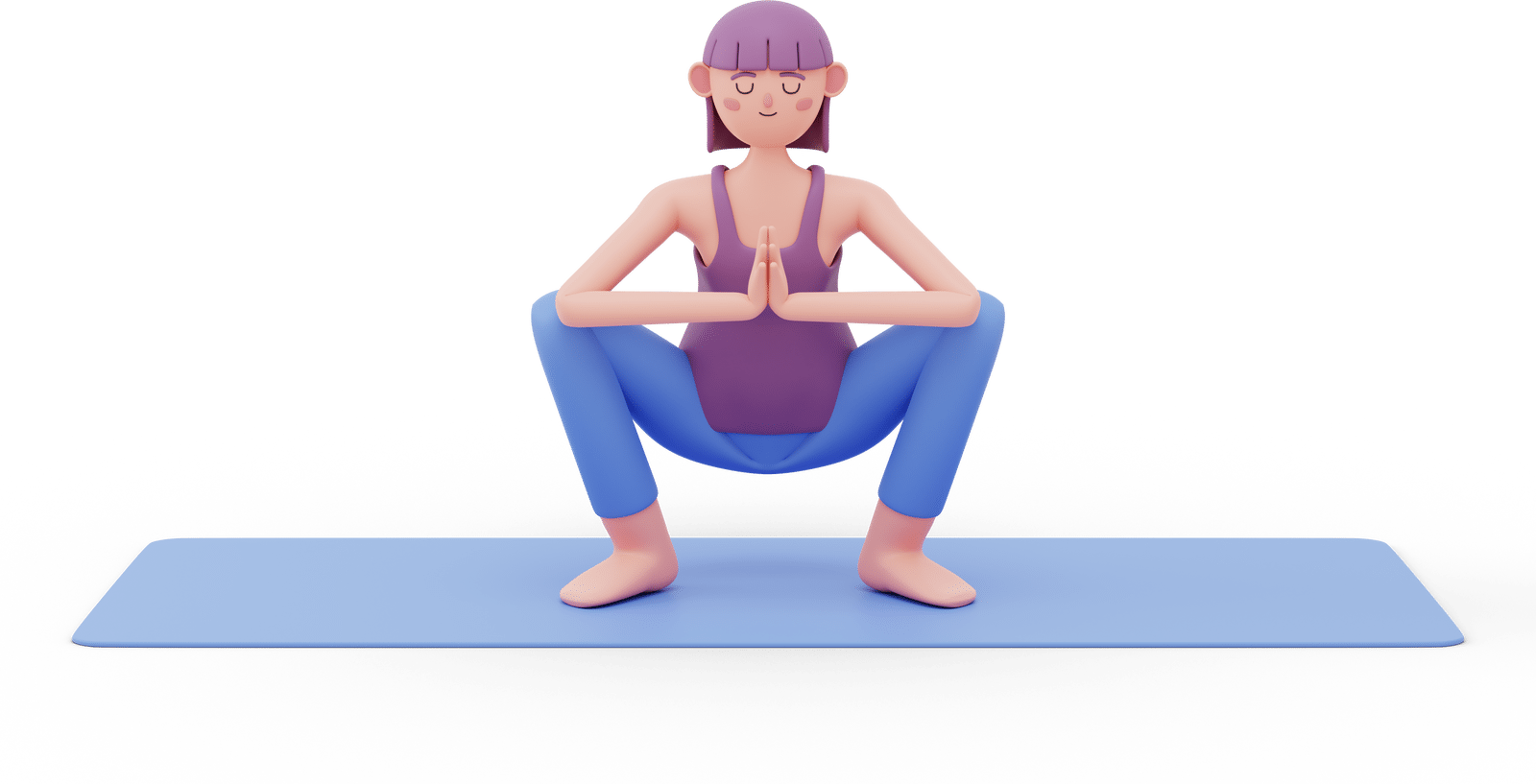
Malasana Pose: A deep squat that targets the pelvic floor, hips, and lower back.

Reclined Bound Angle Pose: Helps to open the hips and gently stretch the pelvic floor muscles.
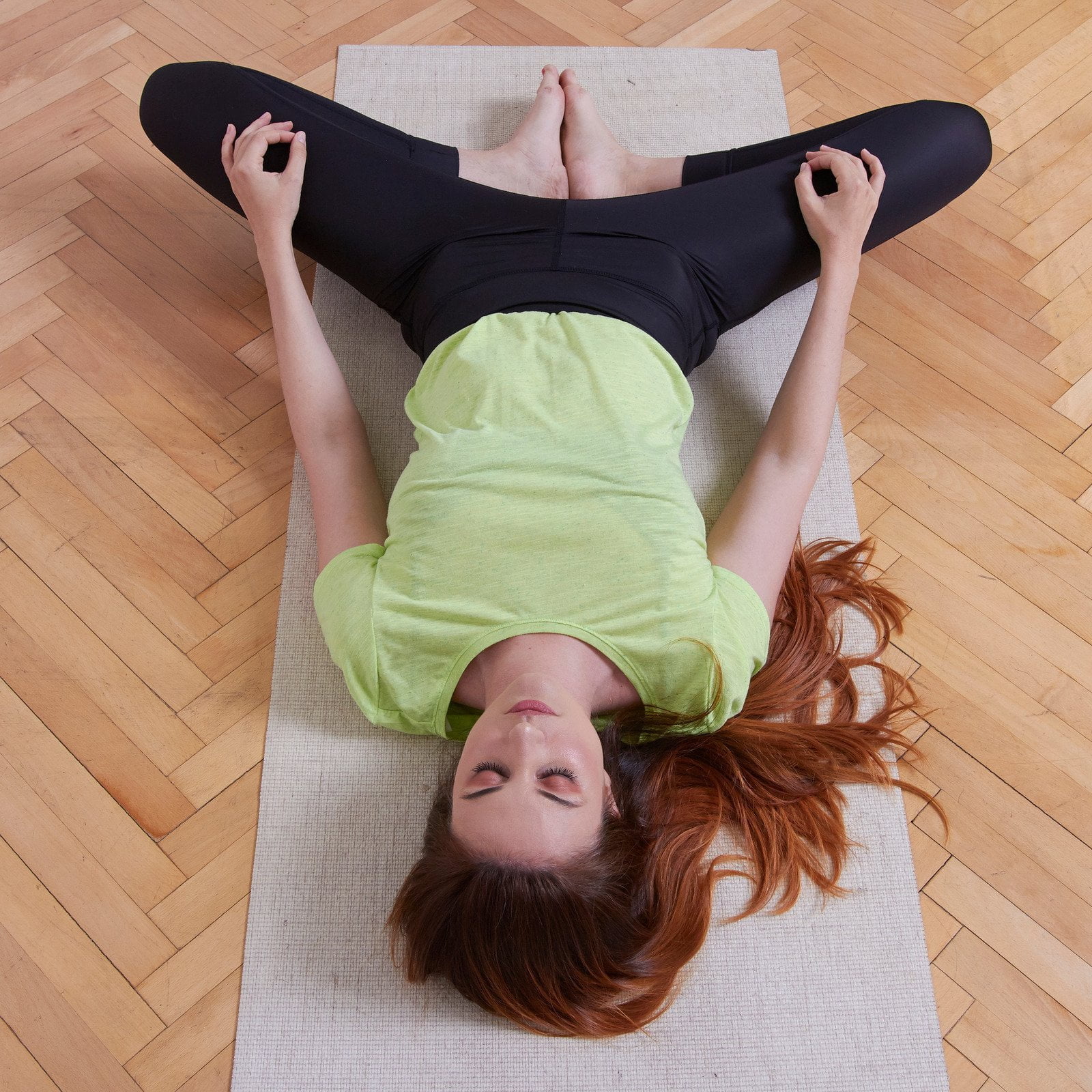

Cat-Cow Pose: Gently stretches and strengthens the pelvic floor muscles while promoting spinal flexibility.


Kegel exercises: Designed to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which support the uterus, bladder, and bowel, as well as contribute to vaginal tightness. These exercises can benefit women who experience urinary incontinence, reduced vaginal sensation, or pelvic organ prolapse. Regularly performing Kegel exercises can help improve vaginal tightness and overall pelvic floor health.

Squats and lunges: Functional exercises like squats and lunges can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles by targeting the surrounding muscle groups, such as the glutes and thighs. Ensure proper form when performing these exercises to avoid strain or injury.